From 2D to 6-Axis: The Evolutionary Map of Robotic Laser Cutting Technology
In the vast cosmos of industrial manufacturing, laser cutting technology has evolved like a shining star, transitioning from rudimentary 2D slicing to the precision of six-axis robotic mastery. Each technological leap has redefined the boundaries of production, transforming not just the degrees of freedom in machinery but revolutionizing;precision, efficiency, and human ingenuity.
1.The 2D Cutting Era: The "Planar Art" of Industrial Revolution
In the 1980s, the commercialization of CO₂ lasers marked the dawn of 2D laser cutting. These systems acted as precise "industrial engravers; slicing through steel plates and acrylic sheets with speeds five times faster than traditional mechanical methods.
Key Features:
Rigid Frameworks:Gantry or cantilever structures with linear X/Y-axis movement.
Flat-Only Processing: Limited to planar materials, unable to handle curves or 3D workpieces.
Industry Impact: Dominated automotive sheet metal and signage markets but required multi-step assembly for complex parts.
Limitations Exposed: By the 2000s, fiber lasers pushed cutting speeds to 60 meters per minute, yet 2D systems struggled with the rising demand for 3D manufacturing, but it also exposed its "inability" to achieve three-dimensional manufacturing.
2.The Rise of 3D Cutting: Shattering Spatial Constraints
Automotive lightweighting and consumer electronics drove demand for 3D laser cutting after 2010. Five-axis systems (X/Y/Z linear + A/C rotary axes) enabled 45° angled cuts on tubes and stamped parts, boosting efficiency by 30% and reducing material waste by 20%.
Breakthroughs:
Dynamic Focusing: Real-time focal tracking on curved surfaces via Z-axis and galvanometer synergy.
Offline Programming: Software like RobotMaster converted CAD models directly into cutting paths.
Case Study: Tesla’s Model S battery tray adopted 3D laser cutting, slashing weld length by 40% and enhancing structural strength by 18%.
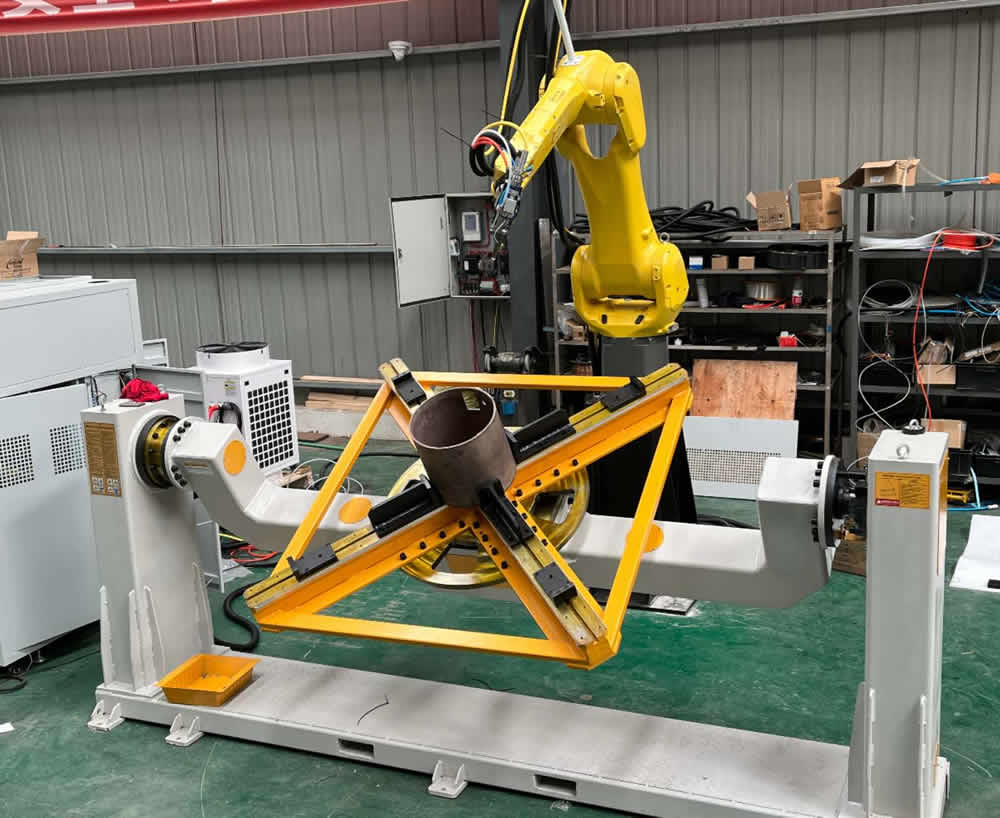

3.Six-Axis Robotics: The Pinnacle of Flexible Manufacturing
When industrial robot giants such as Kuka and FANUC combined six-axis robotic arms with lasers, the manufacturing industry officially entered the era of "omnidirectional cutting". With a repeatability accuracy of ±0.05mm and 360° motion capability, six-axis robots shine in the fields of aerospace engine blades, special-shaped brackets for medical devices, etc.
Key Comparisons:
Dynamic Response
Parameter | 5-Axis | Machine 6-Axis Robot |
Workspace | Fixed processing scope | Spherical radius(2-4m) |
20-50m/min | Up to 200°/s joint speed | |
Cost Efficiency | Single equipment 400,000-700,000 USD | System integration 200,000-450,000 USD |
Innovative Applications:
Spacecraft Fuel Lines:Titanium alloy tubes cut by 6-axis robots replaced brazing, reducing weight by 35%.
Custom Automobile chassis: Force controling sensors enabled "cut-inspect-adjust" loops for low-volume, high-mix production.
4.Drivers of Technology Evolution: Significance Change From Hardware to Intelligence
1) Laser Source Revolution:
Popularization of 10,000-watt fiber lasers. Price of 6KW fiber lasers dropped from $280,000(2015) to $70,000 (2023).
Green/UV lasers tripled cutting speeds for reflective metals like copper.
2) Smart Control Systems:
AI vision achieved ±0.02mm error correction for thermal distortion.
Digital twins slashed trial costs by 90% through pre-cut simulations.
3) Modular Design:
Plug-and-play laser heads, robot arms, and workstations reduced reconfiguration time from 3weeks to 48 hours.
5.Future Horizons: Unlimited Posibilities of 7-Axis Mobility and Ultrafast Lasers
Six-axis robots paired with AGVs create a "seventh axis," liberating systems from fixed workstations. Boston Dynamics’ Stretch robot, equipped with femtosecond lasers, autonomously modifies metal crates in warehouses.
Emerging Trends:
Ultrafast Lasers + 6-Axis Robots: Picosecond lasers carve 20μm vascular channels in cardiac stents with <5μm heat zones.
Human-Robot Collaboration: The lightweight robotic arm is combined with AR glasses, and the worker can generate the cutting path by gesture guidance;
Green Manufacturing: AI-optimized energy use and slag recycling cut carbon emissions by 40%.
Conclusion: Evolution Unleashes Creativity
From 2D precision to six-axis artistry, laser cutting’s evolution embodies humanity’s quest to transcend physical limits. As self-learning 7-axis robots "sculpt" quantum computer heat dissipation structures, we witness the dawn of a "design-to-reality" era—where manufacturing’s only boundary is imagination.
For more information, please click here.
 English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch euskara
euskara Русский язык
Русский язык Italiano
Italiano Português
Português Nederlands
Nederlands Polski
Polski Greek
Greek Lietuva
Lietuva Türkçe
Türkçe 日本語
日本語 한어
한어 中文
中文 தாமில்
தாமில் فارسی
فارسی हिंदी
हिंदी Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Pilipino
Pilipino Indonesia
Indonesia தாமில்
தாமில்